JavaScript Loops: Implementing a while Loop
In the last lecture, we wrote a for loop to display all the odd numbers between 0 and 5. In this lecture, I'm going to show you how to implement the same logic by using a while loop.
Key Learning: for Loop vs. while Loop
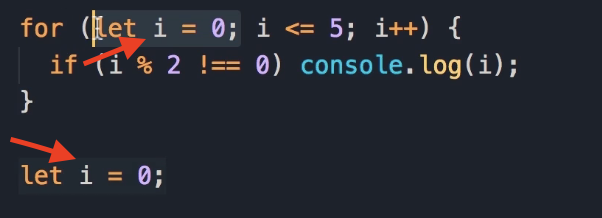
One key difference between a while loop and a for loop is that in for loops, the loop variable is part of the loop itself. But in while loops, you have to declare this variable externally. Let me show you what I mean.
Translating a for Loop to a while Loop
Here is the for loop from the previous lesson that we want to translate:
// Displays odd numbers between 0 and 5
for (let i = 0; i <= 5; i++) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
console.log(i);
}
}
Output:
1
3
5
Here is the step-by-step process to implement that same logic using a while loop.
1. Declare the Loop Variable
We start with declaring a variable like i and set it to 0.
let i = 0;
A Note on Variable Scope
Note that this
iwe have here is different from theiwe have in theforloop, because that variable is only meaningful and accessible inside of thatforloop. This is called scope, and I'm going to talk about it later in the course.All I want you to know is that these two variables are completely different, even though their names are the same.
2. Add the while Statement and Condition
Now, we have our loop variable initialized to 0. Next, we add a while statement. In parenthesis, we need to add our condition. What is the condition here? That is i less than or equal to 5.
while (i <= 5) {
// Statements go here
}
3. Add the Statements to Repeat
Next, we need to add our statements. What is the statement that we want to repeat? We want to display the odd numbers, so we add that here as well.
while (i <= 5) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
console.log(i);
}
}
4. Increment the Loop Variable
Finally, at the end of this while block, we need to increment i.
while (i <= 5) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
console.log(i);
}
i++;
}
Final Code and Execution Flow
So, this is a direct translation of the for loop into a while loop.
Completed while Loop:
let i = 0;
while (i <= 5) {
if (i % 2 !== 0) {
console.log(i);
}
i++;
}
Output:
1
3
5

This is what happens when we execute this code:
-
Initially,
iis 0. -
Now in the
whileloop, first this condition (i <= 5) is evaluated. -
If this condition is true, then the body of the
whileloop will be executed. -
Again, in the next iteration, the condition is evaluated again.
-
If it's true, the statements in the
whileblock will be executed. -
Otherwise, the
whileblock will terminate.
In the next lecture, we're going to look at another kind of loop in JavaScript.