Arrays
Introduction to Arrays
In JavaScript applications, you might need to manage a list of objects, such as:
- Products in a shopping cart.
- Colors selected by a user.
In such cases, an array is an ideal data structure to store these lists.
Declaring and Initializing Arrays
To declare an array, use a meaningful name and initialize it to an empty array using square brackets:
let selectedColors = [];
These square brackets are called array literals, indicating an empty array. You can initialize this array with values:
let selectedColors = ['red', 'blue'];
console.log(selectedColors); // Output: ['red', 'blue']
Understanding Array Indexes
Arrays maintain the order of elements, where each element has an index:
- The index of the first element is 0.
- The index of the second element is 1.
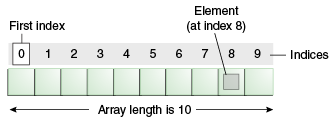
To access an element, use its index:
console.log(selectedColors[0]); // Output: 'red'
Dynamic Nature of JavaScript Arrays
JavaScript is a dynamic language, allowing arrays to change at runtime:
- Dynamic Length: Arrays can grow in size dynamically. You can add elements to an array:
let selectedColors = ['red', 'blue'];
selectedColors[2] = 'green';
console.log(selectedColors); // Output: ['red', 'blue', 'green']
- Dynamic Types: Arrays can store elements of different types. For example, adding a number to an array of strings:
let selectedColors = ['red', 'blue'];
selectedColors[2] = 1;
console.log(selectedColors); // Output: ['red', 'blue', 1]
Arrays are Objects
Technically, arrays are a special type of object in JavaScript:
- Check the type of an array using
typeof:
console.log(typeof selectedColors); // Output: 'object'
- Arrays inherit properties and methods from the
Arrayprototype, such as thelengthproperty which returns the number of elements:
let selectedColors = ['red', 'blue'];
selectedColors[2] = 1;
console.log(selectedColors); // Output: ['red', 'blue', 1]
console.log(selectedColors.length); // Output: 3
Exploring Array Properties
Arrays come with built-in properties and methods that you can access using dot notation. For instance, the length property:
console.log(selectedColors.length); // Output: 3
These properties are automatically inherited from the array prototype.
Summary
Arrays are a powerful and flexible data structure in JavaScript, characterized by:
- Dynamic Length: Arrays can grow or shrink in size.
- Dynamic Types: Arrays can hold elements of different types.
- Inheritance from Object: Arrays are objects and inherit properties and methods from the
Arrayprototype.
In future sections, you will explore various operations and methods associated with arrays. For now, understand that arrays are used to represent lists of items in a dynamic and flexible way.